The complexity of a busy factory shop floor is rather fascinating. It is a system of multiple moving parts, both human and machine, that is expected to turn material into products efficiently, with no trouble and zero incidents.
We all know that humans aren’t perfect, but machines aren’t, either. Because of these imperfections and other factors, such as varying environmental conditions or inconsistent material quality, the system needs constant oversight and correction to avoid machine downtime and run smoothly.
How to Assess Your Losses Due to Machine Downtime
The full scale of losses is much more than the actual time lost during the stoppage. It also includes:
- loss of production that affects the process flow
- scrapped products and wasted raw materials
- overtime wages for extra shifts to catch up with the schedule
- extra maintenance cycles, cost of cleaning-up
Not to mention that the loss is not just financial: taking shortcuts to make up for time lost increases the risk of incidents.
To assess the full impact of downtime, first of all, you need an accurate log of downtime events, and to make the most out of this log, you need to capture all the important details for each event.
What is the data that you need to capture?
Here is what your log of downtime events should include:
- Date and time when the stoppage started
- Duration of the downtime event
- Location (machine, line, part of the line)
- Shift
- The product that was being produced
- Operators who were in charge
- The reason why it happened (ideally – from a list of standardized categories, see a separate article on how to standardize downtime reasons)
- Additional description (for example, comments on the action taken)
What Are the Options and Tools to Track Machine Downtime
1. Manual downtime tracking
If you are not tracking your downtime at all, you can try the simplest method: manual tracking. Its pros are: low budget solution, easy to start with, minimal training required.
Here are a couple of helpful templates:
- Excel spreadsheet template for logging downtime events manually (on paper)
- Google sheet template for analyzing downtime (make a copy to your own Google Drive to edit it)
If you are already tracking downtime manually, then you probably have already realized the cons: it’s time-consuming to enter data and analyze it, the data is not accurate, it can be manipulated by workers, etc. There are so many shortfalls of manual tracking that we have a separate article for that.
The next step is to start using automated tools to record and visualize your downtime.
2. Using a dedicated OEE software solution
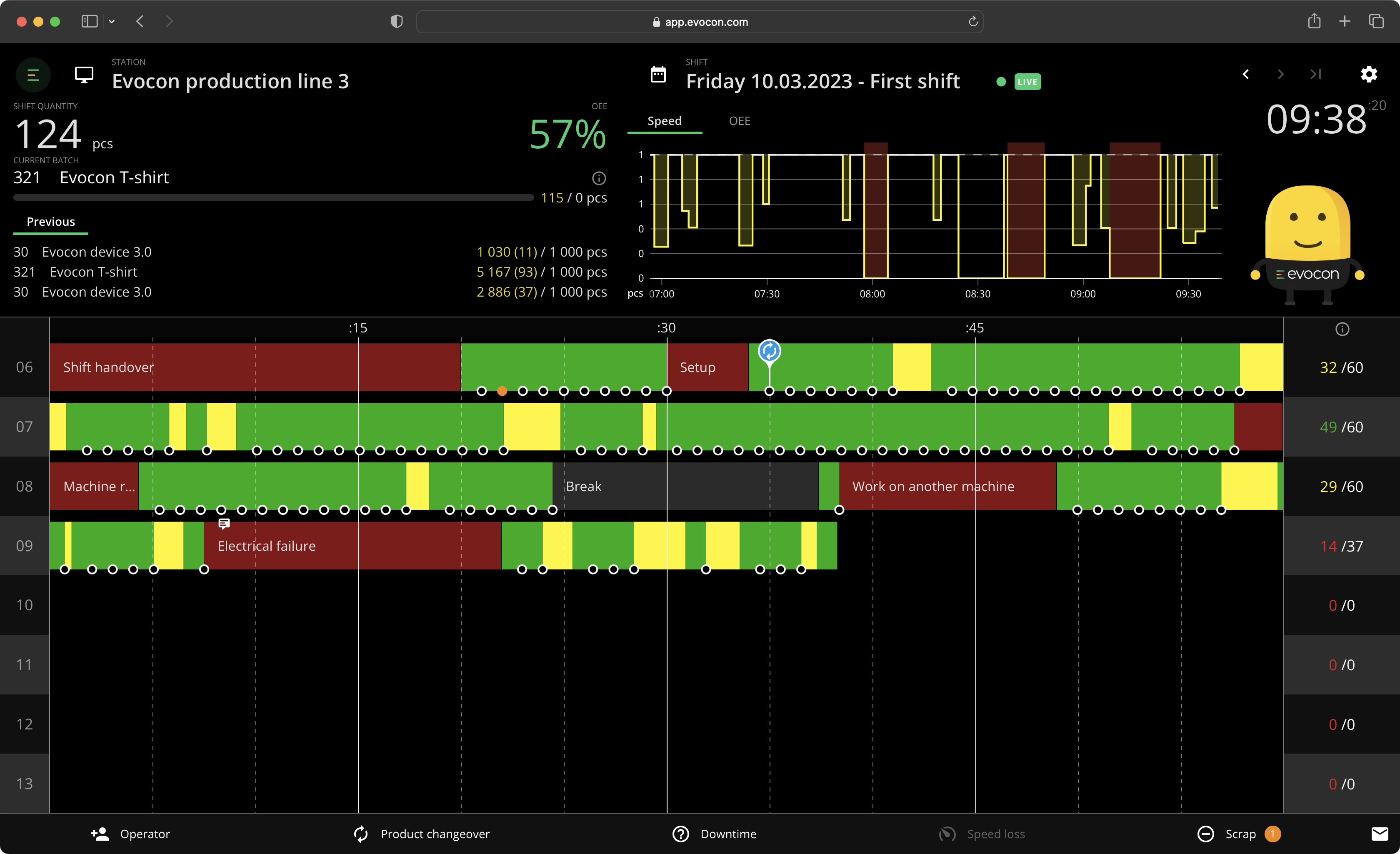
A solution can be considered dedicated if it can:
- Register production in real-time as it is happening (either with sensors and dedicated IIoT devices or by connecting directly to production machines – some machines are capable of providing data about their activity)
- Visualize production data in real-time
- Automatically record data from the machines and store it
- Provide the possibility to enter additional data, such as explanations why downtime occurred
- Provide access to historical data for purposes of analysis
Pros: as you can see from the list above, data captured in this way is accurate and occurs in real-time. You can collect multiple other parameters about the process in addition to downtime.
Dedicated solutions can be on-premise or SaaS (Software as a Service). SaaS solutions have the added benefit of regular updates and new features.
Cons: you need to buy and install it separately, in addition to your other systems. This involves researching available solutions, perhaps trying out a few before you settle on the one that suits you.
Tip: OEE software comparison on Capterra
Dedicated OEE Software
Start measuring and managing your downtime with Evocon’s 30 day free trial.
3. Creating your own in-house solution
This option may be suitable for large companies with specific needs that cannot be covered by existing solutions. For example, integration with company systems is a requirement. Evocon does offer integrations, but other providers may not, or your systems may be very specific.
Pros:
- full control over the solution
- in-house support
- no subscription fees
Cons:
- the cost of development and maintenance has to be covered by only one company
- you need to have an existing IT department capable of building such solutions
- long time to develop the solution: between a few months and a few years
- high maintenance cost
- upkeep of the system can become an issue if a key member of the development team leaves the company
We hope this helps you make the right choice.
Now, how exactly do you reduce downtime once you have the data?
Step-by-step plan to cut downtime by 15%

What Are The Best Practices To Reduce Downtime?
In our article “How to Reduce Machine Downtime and Maximize OEE,” we propose a comprehensive guide for decreasing machine downtime and increasing Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) in the manufacturing industry.
Key strategies include ensuring accuracy in data collection, as it offers a factual understanding of downtime causes and supports strategic problem-solving.
Enhancing visibility of OEE data on the shop floor is encouraged to increase awareness and instigate a culture of continuous improvement. High-frequency or prolonged downtime issues should be prioritized and resolved first for immediate improvements in OEE.
For complex issues, methodologies such as Root Cause Analysis (RCA), Six Sigma, and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) are recommended.
Overall, it’s important to focus of continuous improvement in manufacturing, leverage real-time data, team engagement, and a persistent progress to drive operational excellence.
Summary
We have provided you with a good starting point. Now you know how to assess the impact of machine downtime. We provided some templates to help you with that and an overview of tools and methods you can apply.
To go more in-depth, there are a number of topics to pursue, according to your specific interest. Please go on and browse more of our content – we have quite a library, both on fundamentals of OEE and advice on how to increase your productivity.